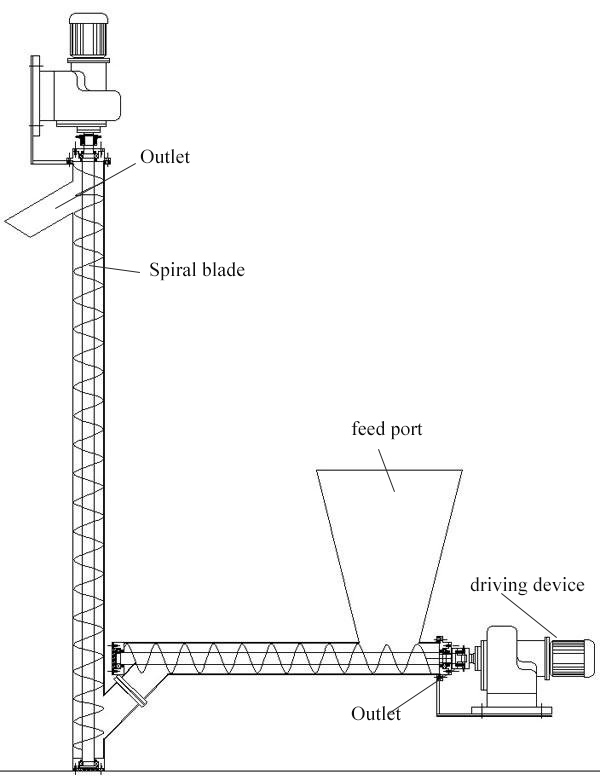
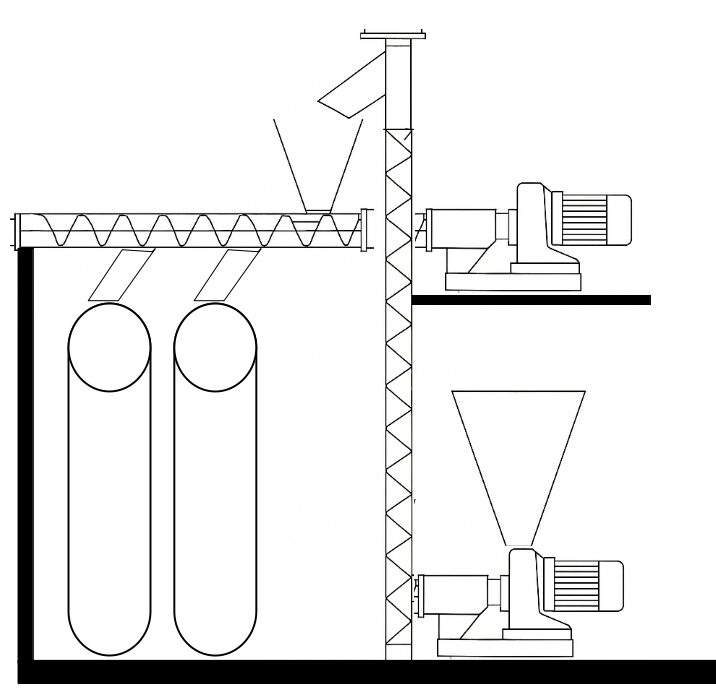
Conveyance Configurations
From precise micro-dosing to high-capacity transfer, we offer auger systems ranging from 1″ to 10″ diameters to suit every application. Whether you need a budget-friendly solution to move just 2 cups of coagulant, or a high-speed system capable of delivering 350 lbs of powder in under 3 minutes, we’ve got the right configuration to match your flow rate, footprint, and budget.
Need Automation? Let us design you a hands-free system!
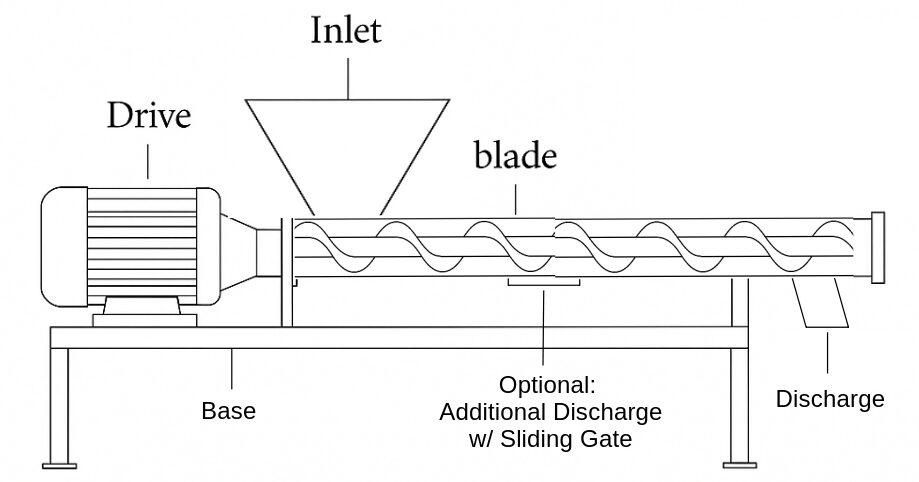
Horizontal Conveyance
Best For:
Consistent feed rate control
Advantages:
Most energy-efficient configuration
Simple to install and maintain
Allows multiple inlets/outlets
Can integrate with hoppers and bins easily
Use Cases:
Transferring dry solids between two points at the same elevation
Dosing systems (due to good metering control)

Vertical Conveyance
Best For:
Lifting material straight up in tight footprints
Advantages:
Maximizes floor space
Ideal for transferring materials to elevated bins, silos, or tanks
Choke-fed = consistent vertical transport
Challenges:
Requires more power
Needs controlled feed to prevent fallback
- Recommended control: continuous feed, choke-fed, VFD, check valve.
Use Cases:
Feeding into reactors, mixers, or silos from a hopper


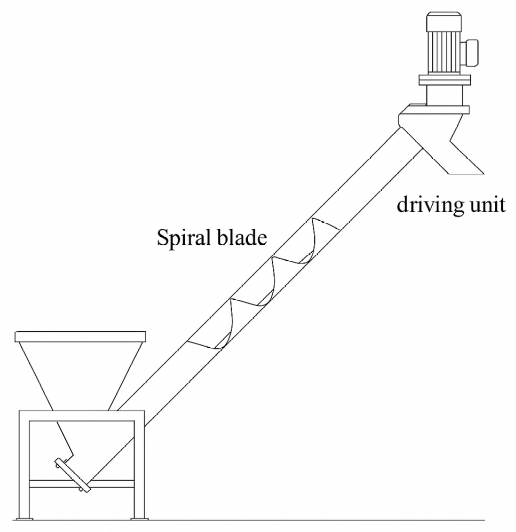
Angled (Incline) Conveyance
Best For:
Combining lift and length in one conveyor
Advantages:
Compromise between horizontal and vertical
Can be gravity-fed or choke-fed depending on angle
Considerations:
Efficiency drops as angle increases (ideal: <45°)
Use Cases:
Feeding mixers, dryers, or intermediate tanks from floor-level bins
Mobile conveyor systems (like bag unloading or batching setups)

Dual-Plane Conveyance
Typically consists of:
Horizontal section → for collection, metering, or transfer
Vertical section → for elevation to discharge point
Best For:
Applications with tight floor space and high discharge elevation
Integrating collection, metering, and elevation in a single system footprint
Advantages:
Compact footprint
Choke-fed vertical section – consistent flow and minimizes fallback
Versatile layout adaptable to a wide range of equipment and plant configurations
Recommended Control Strategy:
Install a VFD (Variable Frequency Drive) for smooth start/stop and speed control
Include a check valve or slide gate to prevent backflow when system is idle
Design for continuous or semi-continuous operation to avoid surging and air gaps
Use Cases:
Transferring powder or granules from a ground-level hopper to an overhead silo, batch mixers or reactors
Compact floor footprint